Financial Instruments Explained: Types and Asset Classes
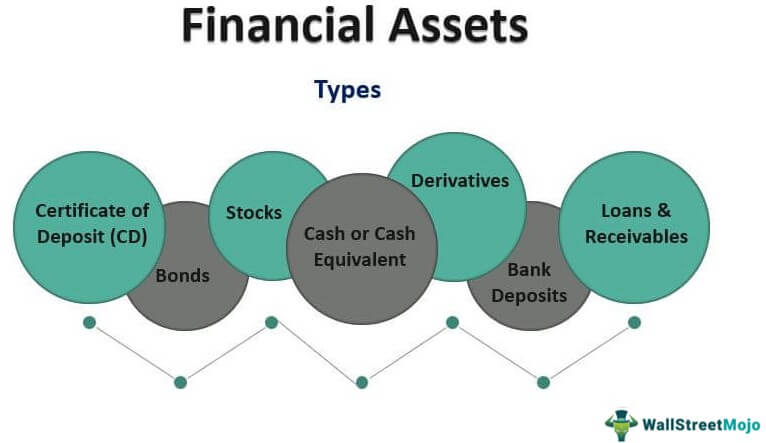
They may provide modest interest income but, unlike equities, they offer little appreciation. Also, CDs and money market accounts restrict withdrawals for months or years. When interest rates fall, callable CDs are often called, and investors end up moving their money to potentially lower-income investments. The purest form of financial assets is cash and cash equivalents—checking accounts, savings accounts, and money market accounts. Liquid accounts are easily turned into funds for paying bills and covering financial emergencies or pressing demands.
Share this:
Assets are also things owed to a business or individual, such as payment for inventory. • Investments, such as stocks and bonds, annuities, mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and so on. Some assets are recorded on companies’ balance sheets using the concept of historical cost.
Derivative Instruments
Aggressive investors seek out companies that are in the early stages of their growth and have a unique value proposition. The Board had always intended that IFRS 9 Financial Instruments would replace IAS 39 in its entirety. However, in response to requests from interested parties that the accounting for financial instruments should be improved quickly, the Board divided its project to replace IAS 39 into three main phases. As the Board completed each phase, it issued chapters in IFRS 9 that replaced the corresponding requirements in IAS 39.
Aggressive, Equities-Focused Portfolio
- It always needs to have a good record of its financial assets list to be put to use whenever needed, like in financial emergencies.
- As the Board completed each phase, it issued chapters in IFRS 9 that replaced the corresponding requirements in IAS 39.
- Insurance companies have different underwriting guidelines, which can affect the maximum age at which they allow policyholders to add this rider.
- Stocks are often considered the riskiest financial assets, but they also offer the greatest potential for growth.
- Alternative investments such as real property, precious metals, and private equity ventures are examples of assets some investors also may choose to use to counter the price movements of a traditional investment portfolio.
- This is beneficial, because historically, stocks, bonds, and alternatives have exhibited less-than-perfect correlations with one another.
A financial asset is a liquid asset that gets its value from a contractual right or ownership claim. Cash, stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and bank deposits are all are examples of financial assets. Unlike land, property, commodities, or other tangible physical assets, financial assets do not necessarily have inherent physical worth or even a physical form.
Financial Assets Examples
However, their pattern of representation, valuation, and impairment is different from other reporting methods. Generally, the Accepted Accounting Principles format is followed in most US-based companies. Rebalancing also may become necessary if the success — or failure — of a particular asset group alters a portfolio’s target allocation.
General recommendations suggest having three to six months’ worth of living expenses stashed away in an emergency fund — using an account that’s available whenever you need it. Businesses may want to consider using automated asset management systems to track and collect data on their assets. This may be easier than manually tracking assets, which could become complicated and overwhelming.
In general, investors should move toward a conservative asset allocation as their goal date approaches to protect the portfolio’s earnings up to that point. A speculative portfolio is best for investors who have a high level of tolerance for risk. take a closer look at the 2019 home office deduction Speculative plays could include initial public offerings (IPOs) or stocks that are rumored to be takeover targets. Technology or healthcare firms in the process of developing a single breakthrough product also would fall into this category.
In business, assets are resources owned by a business that have economic value. They might refer to the building the business owns, inventory, accounts receivable, office furniture, and computers or other technology. Financial assets refer to securities or assets such as stocks, bonds, certificates of deposit (CDs), and preferred equity. Assets are basically anything of value that an individual, a business enterprise, or another entity owns. Different types of assets are treated differently for tax and accounting purposes. Generally speaking, assets are a good thing to have, and liabilities less so.


